Becoming a secondary school teacher through the Teachers Service Commission (TSC) is a prestigious achievement in Nepal’s education sector. To ensure that candidates meet the highest teaching standards, TSC conducts a Secondary Level Teaching Permit Exam, which evaluates a candidate’s knowledge, teaching aptitude, and proficiency in the relevant subject areas. This article provides a comprehensive breakdown of the syllabus, exam structure, and preparation tips for aspiring candidates.
Secondary Level Teaching Permit Exam Syllabus
The secondary level teaching permit exam is essential for individuals seeking a teaching position in secondary schools. The exam focuses on a candidate’s ability to teach specific subjects, implement effective teaching methodologies, and understand the national curriculum.





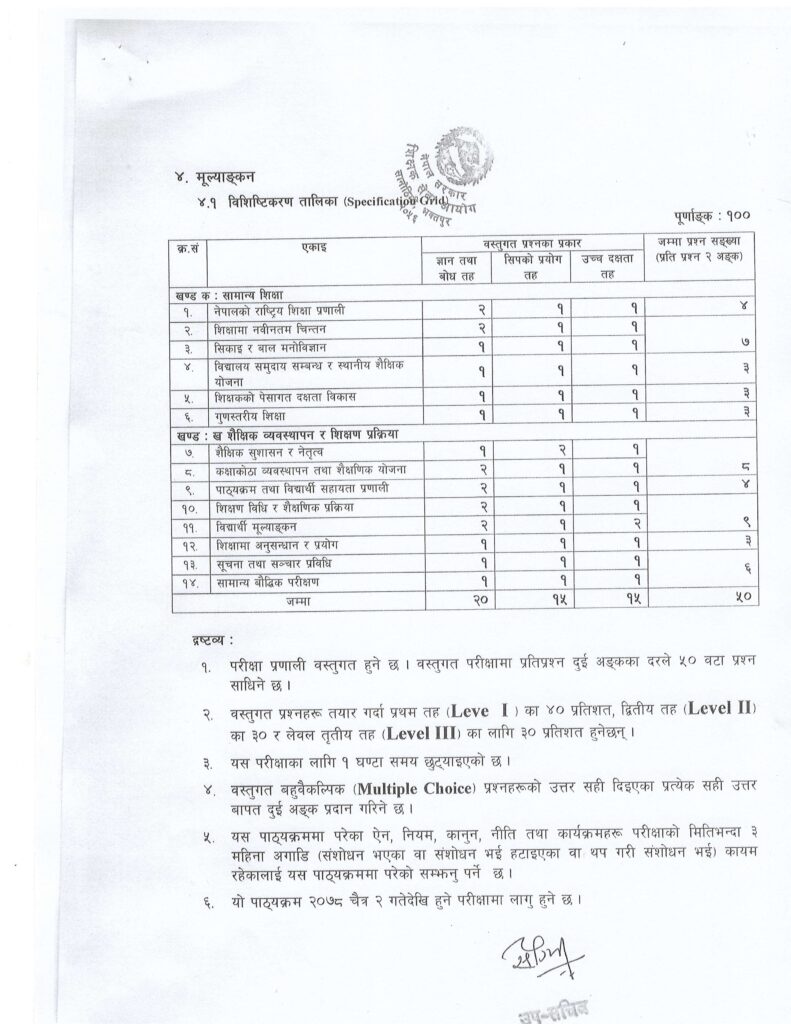
Detailed Syllabus for the Secondary Level Teaching Permit Exam
1. Pedagogical Knowledge
Pedagogy forms the foundation of the exam, focusing on teaching strategies and classroom management.
Key Topics:
- Child Psychology and Development: Understanding adolescent psychology and cognitive development stages.
- Teaching Methods and Strategies: Activity-based learning, collaborative teaching, and problem-solving approaches.
- Lesson Planning: Components of effective lesson plans, learning objectives, and assessment integration.
- Classroom Management: Techniques to handle discipline, foster engagement, and create an inclusive environment.
- Educational Assessment and Evaluation: Types of assessments, formative vs. summative evaluations, and feedback mechanisms.
2. Subject-Specific Knowledge
Candidates must demonstrate a deep understanding of the subject they intend to teach. Here are the major subjects and their key topics:
English
- Grammar and composition.
- Literature analysis and interpretation.
- Teaching English as a Second Language (TESL) strategies.
- Developing reading, writing, and speaking skills.
Mathematics
- Algebra, geometry, and trigonometry.
- Statistics and probability.
- Mathematical problem-solving techniques.
- Teaching methodologies for abstract concepts.
Science
- Physics: Mechanics, optics, and thermodynamics.
- Chemistry: Atomic structure, periodic table, and chemical reactions.
- Biology: Human anatomy, ecology, and genetics.
- Environmental Science: Conservation, sustainability, and climate change.
Social Studies
- History and culture of Nepal.
- Geography and natural resources.
- Political systems and governance.
- Economic principles and sustainable development.
Nepali
- Grammar and vocabulary.
- Creative and formal writing.
- Nepali literature and its teaching methodologies.
3. Curriculum Knowledge
Candidates must be familiar with the secondary education curriculum in Nepal.
Key Topics:
- National Curriculum Framework: Objectives, competencies, and outcomes for secondary education.
- Textbook Analysis: Understanding prescribed textbooks and their alignment with the curriculum.
- Curriculum Implementation: Integrating national standards into lesson delivery.
- Educational Trends: 21st-century teaching skills, digital integration, and global perspectives.
4. Educational Policies and Practices
Understanding Nepal’s education system and policies is crucial for aspiring teachers.
Key Topics:
- Education Policies of Nepal: TSC guidelines, teacher roles, and responsibilities.
- Inclusive Education: Strategies to address the needs of diverse learners, including those with disabilities.
- Professional Ethics for Teachers: Maintaining integrity, fairness, and professionalism in education.
- School Governance: Roles of teachers in administrative tasks and parent-teacher collaboration.
5. ICT in Education
The use of technology in teaching is an important skill for modern educators.
Key Topics:
- Basic Computer Skills: Using word processors, spreadsheets, and presentation tools.
- Digital Tools for Teaching: E-learning platforms, interactive whiteboards, and virtual classrooms.
- Cybersecurity: Protecting data and ensuring ethical use of technology.
- Blended Learning: Combining traditional and digital methods for effective teaching.
6. General Knowledge and Current Affairs
This section evaluates candidates’ awareness of recent developments in education and broader global issues.
Key Topics:
- Educational Innovations: New trends and technologies in teaching.
- National and International Current Affairs: Recent events impacting education.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Focus on education-related goals.
- Constitution of Nepal: Rights, responsibilities, and governance structure.
Preparation Strategies for the Secondary Level Teaching Permit Exam
1. Understand the Syllabus Thoroughly
Begin your preparation by analyzing the syllabus and creating a checklist of all the topics.
2. Develop a Study Plan
Organize your study time effectively by allocating specific time slots for each section.
3. Focus on Pedagogy
Strengthen your understanding of teaching methods, classroom management, and educational assessments.
4. Enhance Subject Knowledge
Deepen your expertise in the subject you wish to teach. Use textbooks, online resources, and previous year question papers for reference.
5. Stay Updated
Keep up with current affairs and trends in education by reading newspapers, journals, and online articles.
6. Practice Digital Skills
Familiarize yourself with technology tools and digital platforms that enhance classroom learning.
7. Take Mock Tests
Regularly practice mock exams to improve time management and identify areas of improvement.
8. Join Study Groups
Collaborate with peers to share knowledge, discuss topics, and clear doubts.
Common Challenges and Solutions
1. Difficulty in Managing Time
- Solution: Use a planner or timetable to balance study time for each section.
2. Fear of Practical Demonstrations
- Solution: Practice delivering lessons to a mock audience and seek constructive feedback.
3. Lack of ICT Knowledge
- Solution: Enroll in short-term computer courses or watch online tutorials to enhance digital skills.
Why Choose a Career in Secondary Teaching?
- Impactful Profession: Shape the future of students by imparting knowledge and life skills.
- Job Stability: Enjoy long-term security and benefits in government positions.
- Personal Growth: Continuously evolve through professional development and interactions with students.
- Career Progression: Opportunities for promotion and specialization in your subject area.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the minimum qualification for the TSC secondary level teaching permit?
A1: A Bachelor’s degree in Education (or equivalent) and a teaching license are mandatory.
Q2: How can I excel in the teaching demonstration?
A2: Prepare detailed lesson plans, practice delivering lessons, and focus on engaging students with interactive methods.
Q3: Is there negative marking in the written exam?
A3: This depends on the exam guidelines issued by TSC. Review the official notification for specifics.
Q4: How important is general knowledge in the exam?
A4: General knowledge contributes significantly to the overall score and demonstrates your awareness of current events and policies.
Q5: Where can I find study materials for the exam?
A5: Use TSC-recommended resources, textbooks, online courses, and mock tests for preparation.
The TSC Secondary Level Teaching Permit Exam requires dedication, thorough preparation, and a deep understanding of both pedagogy and subject knowledge. By following this guide and adopting effective study strategies, you can achieve success and embark on a fulfilling teaching career.