Discover simple and reliable ways to find the nameserver of any website. Use tools like DNS lookup, Who is, and command-line utilities to uncover accurate domain details for troubleshooting and management.
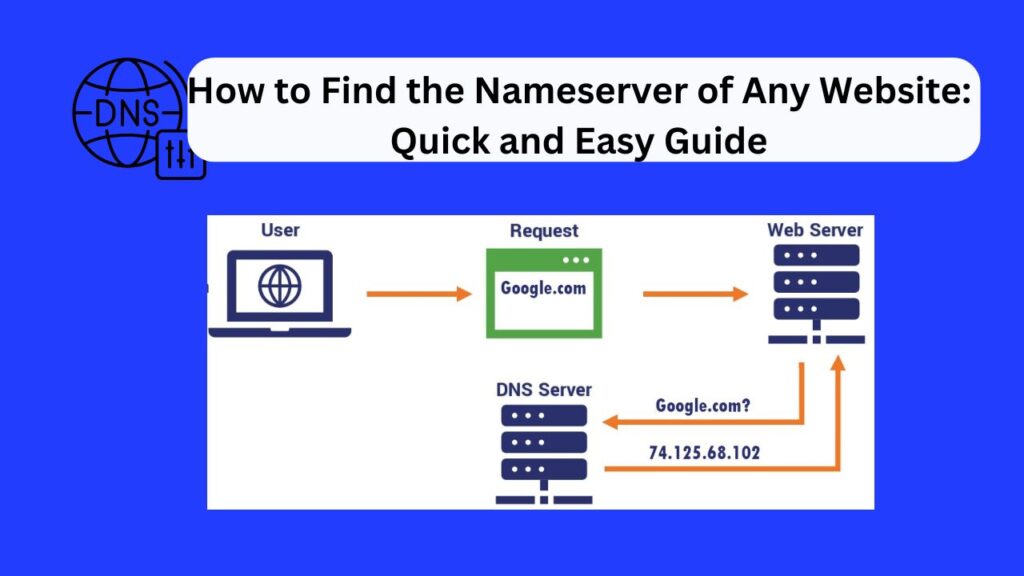
The Domain Name System (DNS) plays a crucial role in the Internet ecosystem, with nameservers acting as an essential component. Nameservers connect domain names to hosting servers, ensuring smooth web navigation. Whether you’re troubleshooting a website issue, migrating a domain, or simply curious, knowing a website’s nameserver can be immensely helpful.
In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about finding the nameserver of any website.
What Are Nameservers?
Nameservers are specialized servers that handle DNS queries, translating domain names (e.g., example.com) into IP addresses. This process allows browsers to load the appropriate website hosted on the server linked to that domain.
For instance, when you type www.google.com, a nameserver tells your browser the correct IP address of Google’s server, enabling the connection.
Why Might You Need to Know a Website’s Nameserver?
Knowing a website’s nameserver can be important for several reasons, depending on the context. Here are the main scenarios where you might need to know a website’s nameserver:
1. Domain Management
- DNS Configuration: If you manage a domain, you must know its nameservers to configure DNS records (e.g., A, CNAME, MX, or TXT records) correctly. These records control your domain’s interaction with hosting, email services, and other online tools.
- Changing Hosting Providers: When switching web hosts, you often need to update the nameservers to the new hosting provider.
2. Troubleshooting Website Issues
- Website Down or Not Resolving: If a website is not accessible, checking its nameservers can help determine if DNS misconfiguration or propagation issues are the cause.
- Diagnosing Propagation Delays: Understanding where the nameservers point can help diagnose delays when updating DNS records.
3. Security and Ownership Verification
- Domain Ownership: Nameservers can provide clues about who controls a domain. This is helpful for verifying ownership or tracking down the current domain registrar.
- Detecting Hijacking or Misconfiguration: Incorrect or unexpected nameservers might indicate unauthorized changes or security issues.
4. SEO and Website Performance
- Website Hosting Analysis: Nameservers can reveal details about the hosting provider, which might influence website speed, uptime, or SEO rankings.
- DNS Performance Optimization: If a website is experiencing slow DNS resolution, understanding the nameserver configuration can help improve performance by switching to faster DNS providers.
5. Competitor Research
- Understanding Hosting Choices: For businesses, knowing the nameservers of competitor websites can provide insight into their hosting providers or CDN usage (e.g., Cloudflare).
6. Email Configuration
- Email Service Setup: Nameservers direct DNS queries, including those for MX records, which control email delivery. Incorrect nameserver configurations can lead to email delivery issues.
How to Find the Nameserver of Any Website
Here are four reliable methods to discover a website’s nameservers:
1. Using Online Tools
Online tools make it simple to fetch information of nameserver of any website without technical expertise.
- WHOIS Lookup Services:
Websites like whois.net or ICANN Lookup display WHOIS information, including nameservers.
Steps:
- Visit a WHOIS lookup website.
- Enter the domain name in the search bar.
- Review the nameservers displayed in the results.
- DNS Checker:
Tools like dnschecker.org allow you to query DNS records, including nameservers.
Steps:
- Go to the website.
- Select the “NS” (Nameserver) record type.
- Enter the domain name and click “Search.”
2. Using Command-Line Tools
For tech-savvy users, command-line tools provide a straightforward way to check nameservers.
- Windows Command Prompt:
- Open Command Prompt (cmd).
Run the command:
nslookup -type=ns [domain]
- Replace [domain] with the desired website (e.g., example.com).
- Linux/Mac Terminal:
- Open the Terminal.
Run the command:
dig [domain] NS
- Example: dig example.com NS.
- PowerShell (Windows):
- Open PowerShell.
Run the following command:
Resolve-DnsName -Name [domain] -Type NS
3. Checking Web Hosting Dashboards
If you have access to the hosting account linked to a domain, you can find nameserver details in the DNS settings.
Steps:
- Log in to your hosting provider’s dashboard (e.g., GoDaddy, Bluehost).
- Navigate to the domain management or DNS settings section.
- Look for nameserver information, which may appear as ns1.examplehost.com, ns2.examplehost.com, etc.
4. Using Browser Extensions
Browser extensions simplify the process of checking nameservers without needing additional tools.
Examples include:
- DNS Lookup (available for Chrome and Firefox).
- Whois Lookup extensions.
Steps:
- Install the extension.
- Visit the target website.
- Use the extension to view DNS or nameserver details.
Tips for Accurate Results
To get accurate results when checking a website’s nameservers or diagnosing related issues, follow these tips:
1. Use Reliable Tools
- Online DNS Lookup Tools: Use trusted tools like MXToolbox, DNS Checker, or Whois Lookup.
- Command Line Utilities: Use tools like nslookup, dig, or whois on your terminal for accurate and detailed results.
2. Query Authoritative Nameservers
- Always query authoritative nameservers directly if possible, as they hold the most up-to-date and reliable information about the domain.
3. Be Mindful of DNS Propagation
- Changes to nameservers or DNS records can take up to 48 hours to propagate globally. Check results from multiple locations using tools like DNS Checker to verify changes.
4. Verify the Domain Registrar
- Check the domain’s registrar’s website to confirm the correct nameservers. Most registrars provide a dashboard or support documentation showing the nameservers for their domains.
5. Double-Check Spelling and Syntax
- Ensure there are no typos in domain names or DNS commands. A small error can lead to incorrect results or querying the wrong domain.
6. Account for Caching
- Cached DNS information can lead to outdated results. Use dig +trace or similar options to bypass caching and get accurate results from authoritative sources.
7. Use Multiple Sources
- Cross-check nameserver information using multiple tools or services to ensure consistency. Results from one source might not reflect recent updates or changes.
8. Pay Attention to TLD-Specific Rules
- Some top-level domains (TLDs) have specific rules or restrictions for nameservers. Make sure the nameservers comply with the TLD’s requirements.
9. Validate with the Hosting Provider
- Confirm the nameservers with the hosting provider or DNS service to ensure the correct settings. Sometimes, hosting changes require nameserver updates.
10. Monitor for DNS Propagation Status
- Use tools like WhatsMyDNS to track the status of DNS propagation worldwide, ensuring changes are taking effect.
FAQ: Nameservers and DNS
- What happens if a domain has incorrect nameservers?
- The domain will not properly connect to its hosting server, leading to website inaccessibility.
- Can nameservers reveal hosting provider information?
- Yes, nameservers often indicate the hosting provider (e.g., ns1.bluehost.com typically points to Bluehost).
- Is it legal to check the nameserver of another website?
- Yes, nameserver information is publicly accessible and part of DNS records. However, always use this information responsibly.
Conclusion
Knowing the nameserver of a website is valuable for troubleshooting, domain management, and understanding a domain’s setup. Nameservers play a critical role in the functionality of websites, email systems, and other online services. Whether you’re addressing connectivity issues, transferring a domain, or optimizing performance, having accurate nameserver information is essential.
By using reliable tools, verifying data, and understanding DNS propagation, you can efficiently manage and troubleshoot domain-related tasks. These methods are accessible to both beginners and advanced users, providing quick and reliable ways to uncover this crucial information.
