Introduction
The Primary Level Teaching Permit Exam, conducted by the Teachers Service Commission (TSC), is a crucial step for individuals aspiring to teach at the primary school level. This examination evaluates candidates’ knowledge of pedagogy, educational policies, subject expertise, and classroom management. Preparing effectively requires a thorough understanding of the syllabus, which serves as the foundation for achieving success in this competitive test.
In this article, we will provide a detailed overview of the Primary Level Teaching Permit Syllabus, focusing on the key topics and tips for effective preparation.
Syllabus
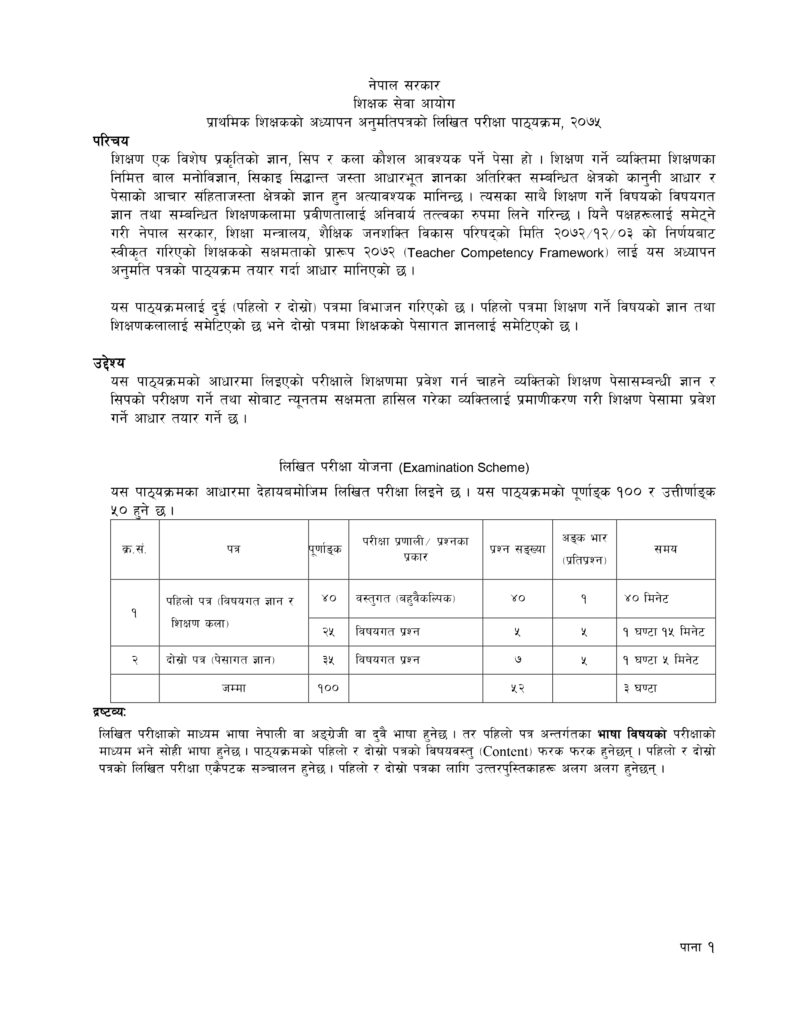


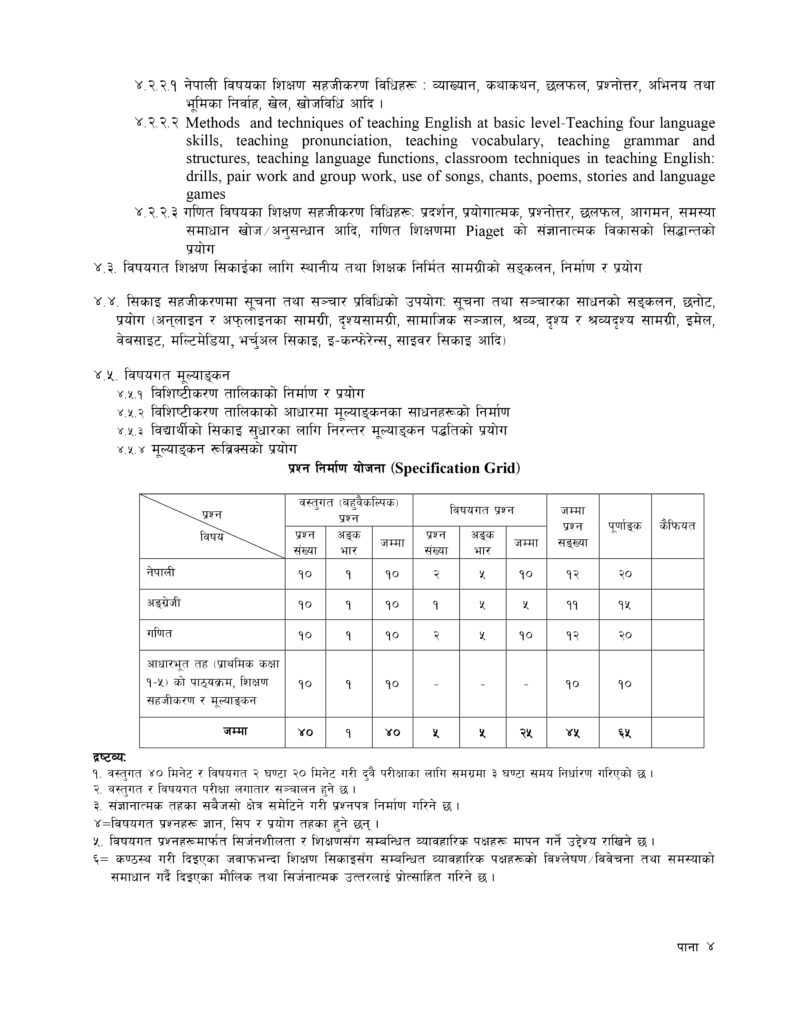


Primary Level Teaching Permit Syllabus Overview
The syllabus for the Primary Level Teaching Permit Exam is designed to ensure candidates possess the necessary skills and knowledge to provide quality education to young learners. The syllabus is divided into the following key sections:
- Pedagogy and Child Psychology
- Nepali Language
- English Language
- Mathematics
- Science
- Social Studies
- General Knowledge and Current Affairs
1. Pedagogy and Child Psychology
This section assesses the candidate’s understanding of teaching methodologies, classroom management, and child development principles.
Key Topics:
- Child Development:
- Stages of physical, cognitive, and emotional development in children.
- Theories of child development (Piaget, Vygotsky, Erikson).
- Learning Theories:
- Behaviorism, Constructivism, and Socio-Cultural learning theories.
- Bloom’s Taxonomy and its application in teaching.
- Teaching Methods:
- Lecture, discussion, activity-based, and inquiry-based learning.
- Use of teaching aids and technology in classrooms.
- Classroom Management:
- Techniques for maintaining discipline and encouraging participation.
- Strategies to handle diverse learners, including children with special needs.
- Assessment and Evaluation:
- Formative and summative assessments.
- Methods to evaluate student performance effectively.
Preparation Tips:
- Read books on educational psychology and pedagogy.
- Practice scenario-based questions on classroom management.
- Stay updated on innovative teaching practices.
2. Nepali Language
This section evaluates proficiency in the Nepali language, focusing on grammar, comprehension, and creative writing.
Key Topics:
- Grammar:
- Sentence structure, tenses, and punctuation.
- Use of sandhi, samasa, and alankar in Nepali.
- Comprehension:
- Reading passages and answering related questions.
- Analyzing the main idea and themes of the text.
- Creative Writing:
- Essay, letter, and story writing.
- Writing applications and notices in formal Nepali.
Preparation Tips:
- Practice Nepali grammar exercises regularly.
- Read Nepali literature and newspapers to improve vocabulary and comprehension.
- Write essays and letters to enhance creative writing skills.
3. English Language
The English section assesses the candidate’s command of the language, emphasizing grammar, vocabulary, and communication skills.
Key Topics:
- Grammar:
- Parts of speech, sentence structure, and tenses.
- Use of conjunctions, prepositions, and modals.
- Vocabulary:
- Synonyms, antonyms, idioms, and phrasal verbs.
- Word formation and usage in context.
- Reading Comprehension:
- Analyzing passages for main ideas and details.
- Inferential and critical questions.
- Writing Skills:
- Essay, letter, and paragraph writing.
- Summarizing and paraphrasing techniques.
Preparation Tips:
- Solve grammar practice exercises daily.
- Read English books, articles, and newspapers to expand vocabulary.
- Practice writing essays and summaries.
4. Mathematics
This section focuses on basic mathematical concepts and problem-solving skills relevant to primary education.
Key Topics:
- Arithmetic:
- Operations on numbers (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division).
- Fractions, decimals, and percentages.
- Geometry:
- Basic geometrical shapes, their properties, and measurements.
- Area, perimeter, and volume calculations.
- Algebra:
- Simple equations and inequalities.
- Patterns and sequences.
- Data Interpretation:
- Reading and analyzing graphs, charts, and tables.
- Problem-Solving:
- Word problems related to real-life scenarios.
Preparation Tips:
- Focus on understanding fundamental concepts rather than rote learning.
- Solve sample problems and practice mental math.
- Use visual aids like charts and diagrams to understand geometry better.
5. Science
This section tests the candidate’s knowledge of basic scientific principles and their application in everyday life.
Key Topics:
- Life Science:
- Structure and functions of plants and animals.
- Human body systems and their functions.
- Ecosystems and environmental science.
- Physical Science:
- Basic concepts of matter, energy, and force.
- Simple machines and their applications.
- Earth Science:
- Structure of the Earth, weather, and climate.
- Natural resources and their conservation.
- Scientific Method:
- Steps of scientific inquiry.
- Importance of observation and experimentation.
Preparation Tips:
- Use diagrams and flowcharts for better retention.
- Relate scientific concepts to real-life examples.
- Revise NCERT books or other primary-level science textbooks.
6. Social Studies
This section evaluates the candidate’s understanding of social, historical, geographical, and cultural topics.
Key Topics:
- History and Civics:
- Important events in Nepali and world history.
- Structure and functions of government.
- Geography:
- Physical features of Nepal and the world.
- Natural disasters and their management.
- Culture and Society:
- Festivals, traditions, and cultural diversity in Nepal.
- Social responsibilities and ethics.
Preparation Tips:
- Study Nepali and world history timelines.
- Practice map reading and marking key locations.
- Stay informed about current social and cultural issues.
7. General Knowledge and Current Affairs
This section assesses awareness of current national and international events, along with general knowledge of diverse topics.
Key Topics:
- Current Events:
- National and international news.
- Government policies and education-related updates.
- General Knowledge:
- Key facts about Nepal’s geography, history, and culture.
- Scientific discoveries and technological advancements.
Preparation Tips:
- Read newspapers and follow reliable news portals daily.
- Take quizzes on current affairs and general knowledge.
- Review yearly GK books and magazines.
Tips for Effective Exam Preparation
- Understand the Syllabus:
- Familiarize yourself with each topic and create a study plan.
- Use Standard Resources:
- Refer to TSC-recommended books and primary school textbooks for clarity.
- Practice Regularly:
- Solve previous years’ question papers and sample papers.
- Join Study Groups:
- Collaborate with peers to exchange knowledge and tips.
- Time Management:
- Allocate specific time slots for each subject and stick to the schedule.
- Stay Updated:
- Follow the latest updates on the TSC website regarding the exam pattern and guidelines.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the primary focus of the TSC Primary Level Teaching Permit Exam?
The exam focuses on assessing candidates’ teaching abilities, subject knowledge, and understanding of child psychology to ensure effective teaching in primary schools.
2. Are previous question papers helpful for preparation?
Yes, solving previous question papers helps familiarize candidates with the exam pattern and question types.
3. How important is current affairs knowledge?
Current affairs are vital, as they demonstrate the candidate’s awareness of the world, which is essential for modern teaching.
4. Can non-education graduates appear for the exam?
Yes, non-education graduates with relevant qualifications and a passion for teaching can apply, subject to meeting TSC requirements.
5. How much time should I dedicate to preparation?
A consistent study schedule of 3–4 hours daily for 2–3 months is typically sufficient for effective preparation.
Conclusion
The Primary Level Teaching Permit Syllabus by the Teachers Service Commission is comprehensive, covering essential subjects and skills required for primary education. By understanding the syllabus, focusing on key topics, and following effective preparation strategies, candidates can confidently tackle the exam and move closer to their dream of becoming a primary school teacher.
