The Secondary Level Teaching Exam, conducted by the Teachers Service Commission (TSC) in Nepal, is a gateway for aspiring educators seeking to teach secondary school students. To excel in this competitive exam, candidates must have a thorough understanding of the syllabus, exam structure, and preparation strategies. This guide provides an in-depth look at the TSC secondary level teaching exam syllabus to help you achieve success.
- Syllabus Of Secondary Level Teaching Exam
- Detailed Syllabus for Secondary Level Teaching Exam
- Overview of the Secondary Level Teaching Exam
- Exam Structure and Pattern
- Preparation Strategies for the Secondary Level Teaching Exam
- Common Challenges and Solutions
- Why Choose a Career in Secondary Teaching?
- Frequently Asked Questions
Syllabus Of Secondary Level Teaching Exam
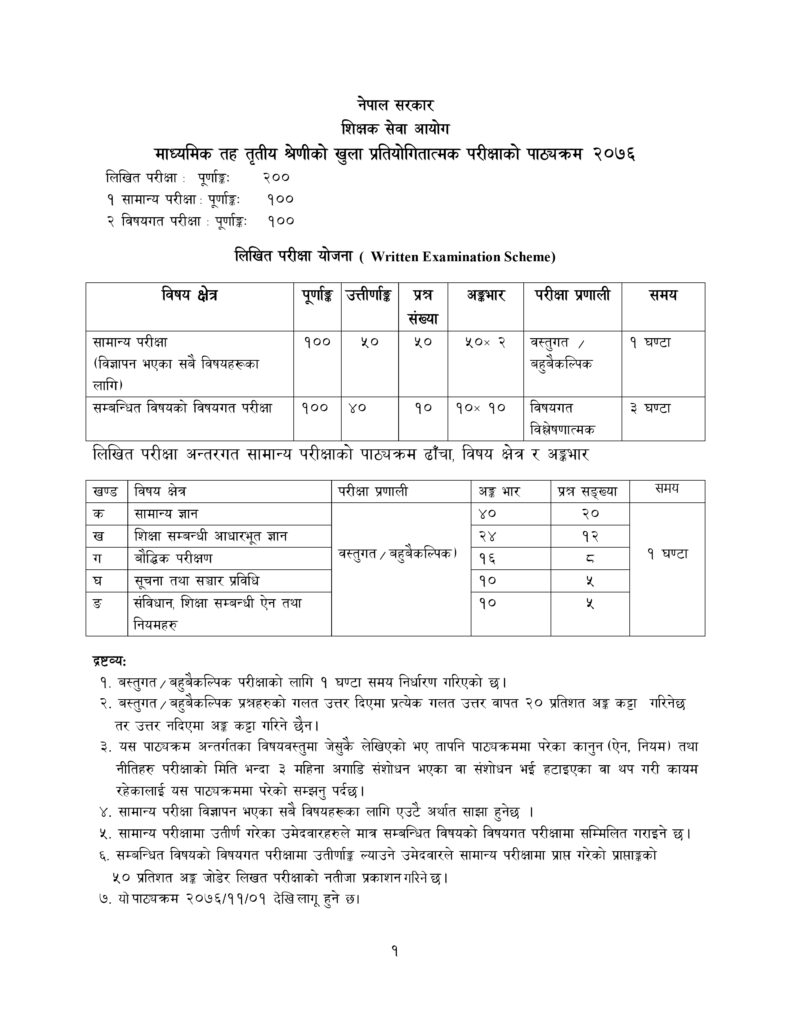




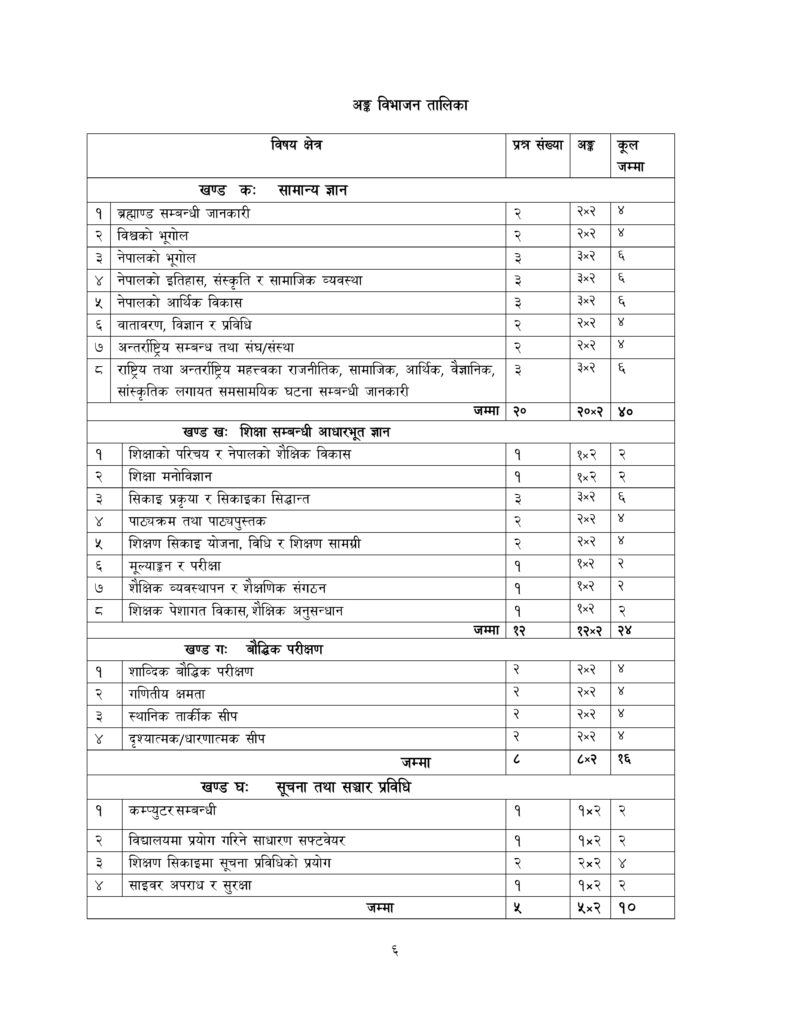
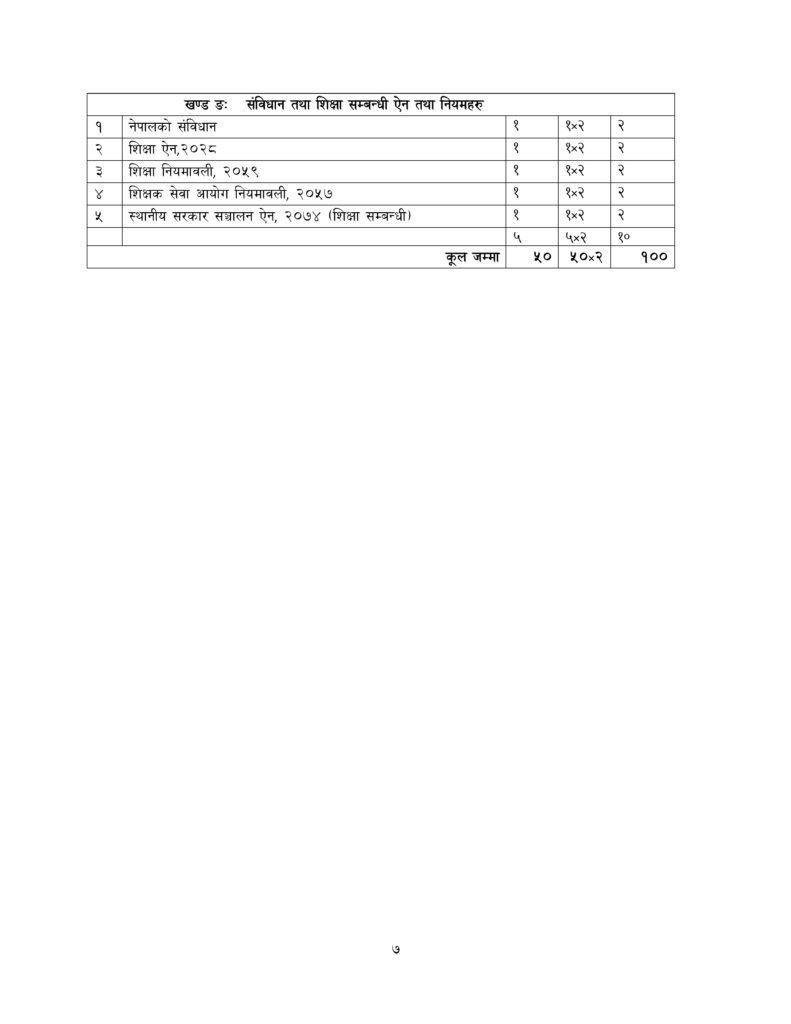
Detailed Syllabus for Secondary Level Teaching Exam
1. Pedagogy and Educational Psychology
This section assesses candidates’ understanding of teaching methodologies and the psychological principles of learning.
Key Topics:
- Child and Adolescent Development: Cognitive, emotional, and social development stages.
- Learning Theories: Behaviorism, constructivism, and socio-cultural theories.
- Teaching Methods: Problem-solving, project-based learning, and cooperative learning strategies.
- Assessment and Evaluation: Types of assessments, formative and summative evaluation, and feedback mechanisms.
- Classroom Management: Techniques to maintain discipline and foster a conducive learning environment.
2. Subject-Specific Knowledge
Candidates are tested on their expertise in the subject they intend to teach. Each subject has its unique set of topics, as outlined below:
English
- Grammar: Sentence structure, tenses, and voice.
- Writing: Essay, letter writing, and report writing.
- Literature: Analysis of poetry, prose, and drama.
- Teaching Techniques: Developing reading, writing, and communication skills.
Mathematics
- Algebra: Linear equations, polynomials, and quadratic equations.
- Geometry: Properties of shapes, theorems, and constructions.
- Trigonometry: Ratios, identities, and applications.
- Statistics and Probability: Data interpretation and basic probability concepts.
Science
- Physics: Motion, force, energy, and optics.
- Chemistry: Atomic structure, chemical reactions, and periodic table.
- Biology: Human anatomy, ecology, and genetics.
- Environmental Science: Conservation, sustainability, and climate change.
Social Studies
- History: Nepalese history and cultural heritage.
- Geography: Physical geography, natural resources, and environmental conservation.
- Civics: Political systems, governance, and the Constitution of Nepal.
- Economics: Fundamental economic principles and sustainable development.
Nepali
- Grammar: Parts of speech, syntax, and sentence construction.
- Literature: Analysis of Nepali prose, poetry, and drama.
- Writing Skills: Essays, reports, and creative writing techniques.
3. Curriculum and Education Policies
Candidates must be well-versed in the educational framework and policies in Nepal.
Key Topics:
- National Curriculum Framework: Objectives, competencies, and implementation strategies for secondary education.
- Education Act and Policies: TSC guidelines, teacher roles, and responsibilities.
- Curriculum Development: Principles, processes, and evaluation.
- 21st-Century Skills: Critical thinking, creativity, and collaboration in teaching.
4. ICT in Education
Technology integration in classrooms is a vital skill for modern educators.
Key Topics:
- Basic Computer Skills: Word processing, spreadsheets, and presentations.
- Digital Tools: Interactive whiteboards, online teaching platforms, and educational apps.
- Blended Learning: Combining traditional and digital methods for effective teaching.
- Cybersecurity: Ethical and secure use of technology.
5. General Knowledge and Current Affairs
This section tests candidates’ awareness of educational developments and general current events.
Key Topics:
- Educational Innovations: Recent trends in education and technology.
- Current Affairs: National and international events.
- Nepalese Constitution: Rights, duties, and governance structure.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Education-focused goals and their implementation.
6. Teaching Aptitude
Teaching aptitude focuses on the candidate’s ability to handle real classroom situations effectively.
Key Topics:
- Effective Communication: Clarity, fluency, and confidence in delivering lessons.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Handling classroom challenges and student issues.
- Adaptability: Modifying teaching methods based on diverse learners’ needs.
Overview of the Secondary Level Teaching Exam
The exam evaluates a candidate’s knowledge, teaching aptitude, and ability to deliver subject-specific content effectively. It emphasizes both theoretical understanding and practical application in teaching secondary-level students.
Exam Structure and Pattern
The exam is generally divided into three stages:
- Written Examination
- Includes multiple-choice questions (MCQs) and descriptive questions.
- Focuses on pedagogy, subject-specific knowledge, and general awareness.
- Practical Examination
- Candidates demonstrate teaching skills, lesson planning, and classroom management.
- Interview
- Evaluates communication skills, understanding of educational policies, and teaching philosophy.
Preparation Strategies for the Secondary Level Teaching Exam
1. Understand the Syllabus Thoroughly
Review the syllabus in detail and identify key topics. Use it as a checklist to track your preparation progress.
2. Create a Study Plan
Allocate specific time slots for each subject and topic. Include time for revision and practice exams.
3. Focus on Pedagogy
Since pedagogy carries significant weight, prioritize learning teaching methods, child psychology, and assessment strategies.
4. Strengthen Subject Knowledge
Deepen your expertise in your chosen subject by referring to textbooks, guides, and online resources.
5. Practice Teaching Demonstrations
Work on lesson planning and classroom interaction. Record your practice sessions for self-assessment.
6. Stay Updated
Read newspapers, follow educational updates, and stay informed about national and international events.
7. Use Digital Tools
Enhance your ICT skills by exploring educational software, e-learning platforms, and digital teaching aids.
Common Challenges and Solutions
1. Time Management
- Challenge: Balancing multiple subjects during preparation.
- Solution: Use a well-structured timetable and focus on high-priority topics.
2. Fear of Teaching Demonstrations
- Challenge: Nervousness during practical exams.
- Solution: Practice in front of peers or mentors and seek constructive feedback.
3. Lack of Digital Skills
- Challenge: Limited knowledge of ICT tools.
- Solution: Take short-term computer courses or watch tutorials on digital tools.
Why Choose a Career in Secondary Teaching?
- Rewarding Profession: Teachers shape future generations and contribute to society.
- Job Stability: Government teaching positions offer long-term security and benefits.
- Opportunities for Growth: Access to professional development programs and promotions.
- Personal Satisfaction: Impact lives by imparting knowledge and values.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are the eligibility criteria for the secondary level teaching exam?
A1: Candidates must have a Bachelor’s degree in Education or a related subject and a teaching license.
Q2: What is the exam duration?
A2: The duration varies but is typically around 3 hours for the written exam.
Q3: How important is ICT for the exam?
A3: ICT is increasingly vital as it evaluates a teacher’s ability to integrate technology into the classroom.
Q4: Are there any recommended books for preparation?
A4: Use TSC-recommended textbooks, pedagogy guides, and subject-specific resources.
Q5: How can I prepare for the interview?
A5: Practice common questions, focus on communication skills, and prepare concise answers about teaching philosophy and educational policies.
The Teachers Service Commission Secondary Level Teaching Exam is a significant step toward a fulfilling career in education. By understanding the syllabus, preparing effectively, and practicing diligently, you can achieve success and contribute to shaping the future of Nepal’s youth. A secondary level teaching permit is required to be a part of the secondary level teaching exam.
